China’s dominance in tea shows no signs of waning

Tea field in Zhejian Province in China. Image: FirsdTea
Amidst a year of increasing global tea production and decreasing exports from producing countries, China continued to lead the pack in production while also taking the second spot in exports. It also remains the dominant source of green teas along with the widest variety of types of tea, including wulong (oolong), white, yellow, and dark teas. Domestic China consumption of teas remains strong, so the forecast for the Middle Kingdom’s tea industry continues to look bright. By Jason Walker
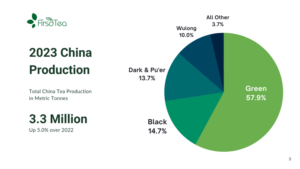
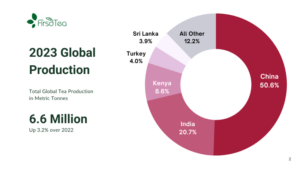
Producing just over one half of the world’s tea in 2023, China remains the world’s dominant tea producer. Global tea production rose by 3.2 percent over the previous year, from 6.4 to 6.6 million metric tonnes (mmt) and the Middle Kingdom accounted for 50.6 percent, or 3.3 mmt while increasing its production by 5 percent over the previous year. India took second place with 20.7 percent of global production, having increased its yield by 2 percent.
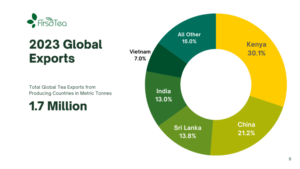
Kenya rounds out the top three producers with 8.6 percent of the world’s annual production. Taken together, these three producers accounted for 80 percent of global production in 2023.
The top four tea-producing countries saw gains in production, including Sri Lanka. Ceylon tea production increased by 1.8 percent after having experienced a tumultuous period of economic struggle and agricultural policies that stymied tea production levels. Argentina, a significant source of black teas for the US market, has seen steady production declines for several years. Argentine tea production decreased by 4.5 percent over 2022 levels. Given historic trends and that the major producers continue to increase their production, overall global tea production levels are expected to continue rising.
All graphs courtesy of FirsdTea
Unlike the other main tea-growing countries, China is primarily a green tea producer: 57.9 percent, or 1.9 mmt of its 2023 production was green tea, followed by 0.49 mmt of black tea. This green tea alone accounts for just under 30 percent of 2023 global tea volume. The remainder of China’s tea is dark (hei) at 13.7 percent, wulong at 10 percent, white at 3 percent, and yellow tea at 0.7 percent. In 2019, black tea surpassed dark tea as the second-largest segment of tea production. Since then, production volumes of the two have remained fairly close. The broader popularity of black tea, along with growing domestic demand for ready-to-drink (RTD) teas and black tea’s relatively high average export price speaks in favour of further gains in black tea production share.
China’s top four tea-producing provinces – Fujian, Yunnan, Sichuan, and Guizhou – accounted for half of China’s tea production, and they each showed increases in production of between 1 and 5 percent. Double-digit gains in production were exhibited by Hubei, the fifth largest producer with a 10.6 percent gain, and Anhui, the eighth largest producer with a 12.4 percent gain. While Fujian may be the single largest tea-producing province, the greatest share of tea is still grown in the Western Belt (35.3 percent from Yunnan, Sichuan, and Guizhou provinces combined) followed by the Eastern Belt (25.7 percent from Fujian, Anhui, and Zhejiang). The Central Belt (Hubei, Hunan, and Shaanxi provinces) follows close behind with 22.2 percent of production.
Fujian may also be China’s top yielding tea province in terms of tons per hectare, but it is only fifth in terms of growing area. Yunnan province leads the pack with over 0.51 million hectares (mha) of tea fields, followed by Guizhou (0.47 mha), Sichuan (0.40 mha) and Hubei (0.38 mha). Fujian’s advantages lie in its warmer climate and more established production areas.
The Chinese government has encouraged the establishment of tea fields in the more poverty-impacted counties of the Central and Western Belts as a means of promoting rural development and strengthening local incomes. Efforts appear to have made progress, as the central government declared victory in eradicating poverty and now aims towards securing more infrastructure development and economic stability. For tea production, however, training these less-experienced workers continues. Outputs are expected to improve along with the maturity of young tea plants and the advancement of tea workers in the areas.
A notable exception is Guangdong province, which has the second highest yield per ha. The province does produce some well-known teas, like yingde black tea and dan cong wulong, but it is generally better known for its industrial output and commercial trade. Guangdong ranks ninth in overall tea production and thirteenth in hectares planted. It shows little sign of dedicating more land to future tea production.
China’s exports dip slightly
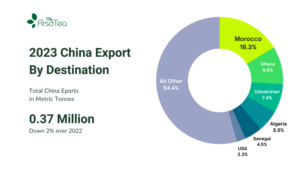
Global tea exports from producing countries declined by about 5 percent over the previous year, with China exports dipping by about 2 percent. China, however, maintained its place as the producing country with the second highest volume of exports. Kenya took the top position, having increased its exports by 14.7 percent over 2022 levels. Kenya accounted for 30.1 percent of global exports from producing countries. China’s 0.37 mmt of exports accounted for 21.2 percent of global exports from producing countries, and 11 percent of China’s annual production.
In terms of volume, 84.2 percent of China’s tea export was green tea and the next highest volume was black tea with 7.9 percent. Green tea exports remained relatively steady compared with 2022 levels, but black tea dropped by 12.6 percent over the previous year. This rise and fall in black export volumes coincided with a few factors. Supply of Ceylon black tea dropped in 2022. When this occurred, Pakistan and other major black tea-importing countries turned to China and others to meet their black tea demands. This surge stands in contrast with what occurred in other parts of the world, where tea imports increased in 2022 as buyers re-stocked after Covid, created supply chain woes, and then decreased their import levels in 2023 as they worked through excess inventory.
Morocco, China’s largest tea-export partner, showed a similar pattern. Most years, Morocco alone takes in about 20 percent of China’s exports, usually around 75,000 metric tonnes. 2020 saw a 9.6 percent decline in Chinese tea imports. The next two years saw import volumes return to usual levels, but 2023 levels declined again by about 16 percent from 75,400 metric tonnes to 59,800 metric tonnes. Ghana, which has been the third largest export destination, increased imports by 44 percent, swapping places with Uzbekistan. Taken together, these three countries import one third of China’s tea exports.
Russia and the United States took in 4 percent and 2.3 percent of China’s exports, respectively. Import volumes were down by 25.1 percent for Russia and 33.7 percent for the US. Overstocking was the main culprit for these declines, particularly for the US. Imports of Chinese teas into the US have been showing signs of rebalancing beginning early in 2024.
A strong outlook
China’s overall tea trends appear positive. Production levels are on track to increase around 4.5 to 5 percent based on average annual increases. Spring 2024 weather in most areas has cooperated, providing a healthy crop thus far. Development in tea producing areas, especially the Western and Central Belts, remains steady. Domestic consumer demand also appears to be on the uptick.
China’s tea industry has been highlighting the need for promoting demand, and recent years have seen an increase in the introduction of bottle teas and other tea-based RTD beverage products. Average export prices can be expected to stay steady between USD $5.50 to $6.00 per kg, although labour and farm inputs (fertiliser, agrochemicals) continue to rise. Export volumes are showing signs of rebounding after last year’s decline. With production and consumption rising, and exports recovering, China is poised to maintain its dominant role in global tea.
- Jason Walker is marketing director of Firsd Tea North America. Prior to his work with Firsd Tea, Walker served in a variety of roles in tea and beverage business capacities. His experience includes business services for small tea companies, a top-ranked online destination for tea consumer education and co-founding a coffee business. His insights draw upon his diverse range of experience in sales, operations and management in the tea world. He may be reached at: [email protected].



